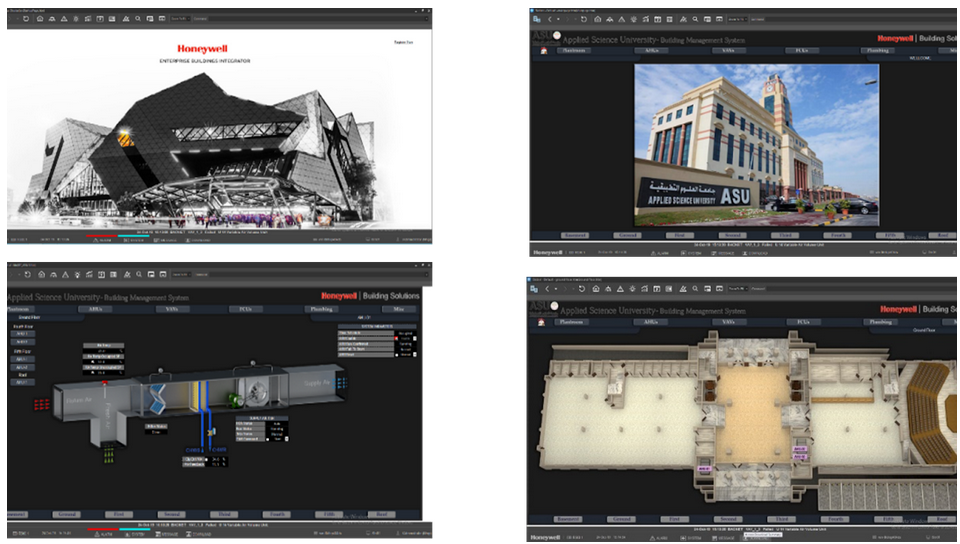
The university has taken several measures towards achieving affordable and clean energy in their buildings. One of these measures is the allowance for maximum daylight penetration into the building through high windows and skylights. This reduces the need for artificial lighting during the day, which saves energy. To prevent the transfer of heat and solar radiation, ASU uses double glazed panels and reflective coatings on out glass. Additionally, the university uses double wall construction with thermal insulation between to cut heat gain and save energy used for cooling. ASU also uses motion sensors in rooms and studios to control artificial lighting, thus saving energy. The university has also switched to using LED light fittings in the main lobby and external facade lighting, which consume less energy than traditional light fittings. Finally, the Building Management System (BMS) controls lightning levels in public areas, optimizing the lightning levels throughout the 24-hour cycle. These measures taken by ASU towards clean and affordable energy not only reduce energy consumption and costs but also contribute to environmental sustainability. The measures taken by the university to reduce energy consumption such as using solar panel streetlights, a Building Management System (BMS), and motion sensors in classrooms, are important steps towards achieving Sustainable Development Goal 7 (SDG 7) – Affordable and Clean Energy. By using solar panel streetlights, the university is promoting the use of renewable energy and reducing its reliance on traditional sources of energy, thus contributing to SDG 7. The BMS by Honeywell EBI-R500 system is also an important tool in reducing energy consumption by optimizing the use of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems on campus. This can help reduce the university’s energy consumption and costs, while also reducing its carbon footprint. Finally, the use of motion sensors in classrooms ensures that energy is not wasted on lighting when the classrooms are not in use, contributing to the overall goal of affordable and clean energy. These measures taken by the university demonstrate its commitment to achieving SDG 7 and promoting environmental sustainability. The Honeywell EBI R500 software is a computer-based control system that consists of both software and hardware components. The software program is typically configured in a hierarchical manner and can be proprietary, utilizing various communication protocols such as C-Bus, Profibus, and others. Vendors are also producing BMS systems that integrate the use of Internet protocols and open standards, including DeviceNet, SOAP, XML, BACnet, LonWorks, and Modbus. Such systems provide enhanced control and management of HVAC systems, improving energy efficiency and contributing to the achievement of Sustainable Development Goal 7 – Affordable and Clean Energy.